Parts of a Computer systems unit
Parts of a Computer system
The motherboard is the main internal hardware component of the system unit. This board is called the “motherboard” because it has all the connectors that connect to the other hardware components of the computer system. This means that all input and output (I/O) devices have their connectors on the motherboard.
Since the CPU (especially high-speed CPU) generates a lot of heat during operation, it has a socket for fixing the central processing unit (CPU) or the processor with a heat sink and fan. It also has a main memory slot, a video or graphics card slot, and a backup battery.
2. CPU or Processor
The CPU is the hardware component responsible for all operations performed in the computer system, which is why most computer users call it the brain of the computer, which is fixed on the motherboard through a slot.
The CPU or processor has two main components, namely the control unit (CU) and the arithmetic logic unit (ALU). CU fetches instructions from memory and executes them to control input and output devices, while ALU performs arithmetic and logic processing. The speed of the processor is measured in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz).
3. RAM
RAM is the main memory of a computer system, and its main function is to temporarily store data. Based on the fact that the data is accessed randomly (in no particular order), it allows the CPU to easily access the data. It can also speed up the operation of the computer because it allows random access to data.
The larger the RAM, the faster the CPU can access data. RAM is volatile, which means it works or stores data while the computer is still running, and loses all data when the computer is shut down. RAM, CPU, and hard disk are the main sources of computer speed. A computer can use multiple RAMs, depending on the user’s preference, but limited by the number of memory slots on the motherboard.
4. Hard Drive
The main storage device of a computer system is a hard disk or hard disk drive. Unlike RAM, which temporarily stores data, the main function of a hard drive is to permanently store information, files, and other documents, and also allows data to be retrieved, but it is non-volatile (data will not be lost when the computer is shut down).
The operating system and application software (apps) are installed on the hard drive. The amount of data that a hard drive can hold depends on its capacity.
Most modern system units or chassis can contain two hard drives, one of which can be used as a “primary” (primary) hard drive; one for installing the operating system, and the other as a “slave” (secondary) hard drive; you can combine documents and Other files are stored on which files and other files to avoid overloading the main hard drive to avoid slowing down the system. The secondary hard drive can also be used as a backup for damage to the primary hard drive.
ROM
ROM (Read-only memory) refers to memory chips storing permanent data and instructions. The data cannot be modified on most ROM chips and is nonvolatile. ROM chips called firmware contain permanently written data, instructions, or information. PROM is a programmable ROM on which a programmer can write permanently. EEPROM is an electrically erasable PROM.
CMOS
Some RAM chips. Flash memory chips, and other memory chips use complementary metal-oxide semiconductors (CMOS) technology because it provides high speeds and consumes little power.
Battery backed CMOS chips keep the date and time even when the computer is turned off.
Types of Computer Ports
Ports are nothing but it is connections between external and internal input/output devices such as keyboards, mice, mouse, Disk Drive, and many more with motherboards using cables. That allows to communicate between external devices or peripherals with a laptop or computer. Computer ports may be virtual or physical. In this article, we are going to discuss about different types of physical computer ports available in the market.
Ports are nothing but it is connections between external and internal input/output devices such as keyboards, mice, mouse, Disk Drive, and many more with motherboards using cables. That allows to communicate between external devices or peripherals with a laptop or computer. Computer ports may be virtual or physical. In this article, we are going to discuss about different types of physical computer ports available in the market.
Characteristics of Ports
There are different characteristics of computer ports:
- External devices like keyboards, mice, and other devices are connected by using computer cables and ports.
- Computer ports are the slots in the motherboard in which cables of the external devices are plugged in for communication.
- Many examples of external devices that can be attached via ports are monitors, mouse, speakers, microphones, keyboards, etc
There are different characteristics of computer ports:
- External devices like keyboards, mice, and other devices are connected by using computer cables and ports.
- Computer ports are the slots in the motherboard in which cables of the external devices are plugged in for communication.
- Many examples of external devices that can be attached via ports are monitors, mouse, speakers, microphones, keyboards, etc
Types of Computer Ports
There are two types of computer ports discussed below:
- Internal port -Internal ports are used to connect internal devices like disk drives, CD drives, and other internal devices with the motherboard.
- External port-External ports are used to connect external devices modem, mouse, printer, flash drives, etc with the motherboard.
Let us now discuss a few important types of ports:
- Serial Port
- Parallel Port
- USB Port
- PS/2 Port
- VGA Port
- Modem Port
- FireWire Port
- Sockets
- Infrared Port
- Game Port
- Digital Video Interface(DVI) Port
- Ethernet Port
Now let us discuss these ports one by one:
There are two types of computer ports discussed below:
- Internal port -Internal ports are used to connect internal devices like disk drives, CD drives, and other internal devices with the motherboard.
- External port-External ports are used to connect external devices modem, mouse, printer, flash drives, etc with the motherboard.
Let us now discuss a few important types of ports:
- Serial Port
- Parallel Port
- USB Port
- PS/2 Port
- VGA Port
- Modem Port
- FireWire Port
- Sockets
- Infrared Port
- Game Port
- Digital Video Interface(DVI) Port
- Ethernet Port
Now let us discuss these ports one by one:
1. Serial Port(COM Port)
A serial port is also called a communication port and they are used for connection of external devices like a modem, mouse, or keyboard (basically in older PCs). Serial cables are cheaper to make in comparison to parallel cables and they are easier to shield from interference. There are two versions of the serial port, which are the 9-pin serial port model and the 25-pin serial port model. The rate of transmission of data in the serial port is 115 KB/sec.
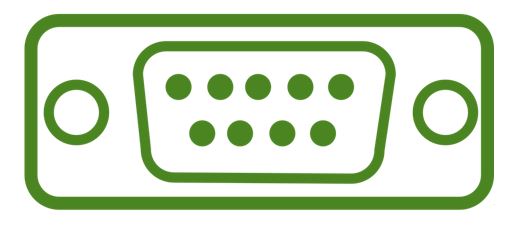
- Serial ports are used for external modems and older computer mice.
- There are two versions of serial-ports that is 9-pin and 25-pin.
- The speed of data in the serial port is 115 kilobits per second.
A serial port is also called a communication port and they are used for connection of external devices like a modem, mouse, or keyboard (basically in older PCs). Serial cables are cheaper to make in comparison to parallel cables and they are easier to shield from interference. There are two versions of the serial port, which are the 9-pin serial port model and the 25-pin serial port model. The rate of transmission of data in the serial port is 115 KB/sec.

- Serial ports are used for external modems and older computer mice.
- There are two versions of serial-ports that is 9-pin and 25-pin.
- The speed of data in the serial port is 115 kilobits per second.
2. Parallel Port (LPT Ports)
Parallel ports are generally used for connecting scanners and printers. It can send several bits at the same time as it uses parallel communication. Its data transfer speed is much higher in comparison with the serial port. It is a 25-pin model. It is also known as Printer Port or Line Printer Port.
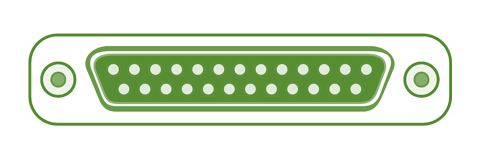
- Parallel Ports are used for scanners and printers
- parallel ports are also known as printer port
- This is a 25-pin model.
Parallel ports are generally used for connecting scanners and printers. It can send several bits at the same time as it uses parallel communication. Its data transfer speed is much higher in comparison with the serial port. It is a 25-pin model. It is also known as Printer Port or Line Printer Port.

- Parallel Ports are used for scanners and printers
- parallel ports are also known as printer port
- This is a 25-pin model.
3. USB (Universal Serial Bus)
In 1997 USB was first introduced. This can connect all kinds of external USB devices, like external hard disk, printer, scanner, mouse, keyboard, etc. There are a minimum of two USB Ports provided in most of the computer systems. It is a kind of new type serial connection Port that is much faster than the old serial Ports These USB Ports are much smarter and more versatile, as they allow the “daisy chaining” of up to 127 USB peripherals connected to one port. The data transfer rate in this is Data12 megabits per second. It also provides plug-and-play communication.

In 1997 USB was first introduced. This can connect all kinds of external USB devices, like external hard disk, printer, scanner, mouse, keyboard, etc. There are a minimum of two USB Ports provided in most of the computer systems. It is a kind of new type serial connection Port that is much faster than the old serial Ports These USB Ports are much smarter and more versatile, as they allow the “daisy chaining” of up to 127 USB peripherals connected to one port. The data transfer rate in this is Data12 megabits per second. It also provides plug-and-play communication.

4. PS/2 Port
PS/2 ports are special ports used for connecting old computer keyboard and mouse. It was invented by IBM. In old computers, there are a minimum of two PS/2 Ports, each for the keyboard and the mouse. It is a 6-pin mini Din connector.
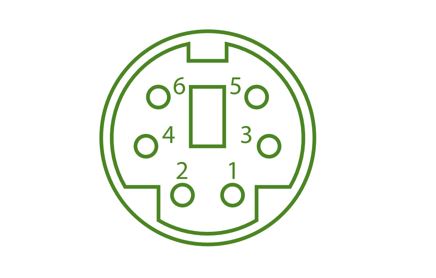
- PS/2 ports are used for old computer keyboard and mouse.
- This is also known as the mouse port.
- Most of the old computers have two PS/2 ports one for the mouse and one for the keyboard.
PS/2 ports are special ports used for connecting old computer keyboard and mouse. It was invented by IBM. In old computers, there are a minimum of two PS/2 Ports, each for the keyboard and the mouse. It is a 6-pin mini Din connector.

- PS/2 ports are used for old computer keyboard and mouse.
- This is also known as the mouse port.
- Most of the old computers have two PS/2 ports one for the mouse and one for the keyboard.
5. VGA Port
VGA ports also known as Video Graphic Array connectors are those which connect the monitor to a computer’s video card. VGA port has 15 holes and it is similar to the serial port connector. But VGA Ports have holes in it and the serial port connector has pins in it.

VGA-Port
- VGA port is used to connects monitor to a computer’s video card.
- There are 15 holes in the VGA port.
- VGA ports are similar to serial port connectors only difference is, that serial connector has pins and VGA has holes.
VGA ports also known as Video Graphic Array connectors are those which connect the monitor to a computer’s video card. VGA port has 15 holes and it is similar to the serial port connector. But VGA Ports have holes in it and the serial port connector has pins in it.

VGA-Port
- VGA port is used to connects monitor to a computer’s video card.
- There are 15 holes in the VGA port.
- VGA ports are similar to serial port connectors only difference is, that serial connector has pins and VGA has holes.
6. Sockets
Microphones and speakers are connected with the help of Sockets to the sound card of the computer.

Microphones and speakers are connected with the help of Sockets to the sound card of the computer.

7. FireWire Port
The IEEE 1394 interface, which is developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s by Apple as FireWire. It can transfer large amounts of data at very high speed. It is used to connect camcorders and video equipment to the computer. It comes up with three variants which are 4-Pin FireWire 400 connector, 6-Pin FireWire 400 connector, and 9-Pin FireWire 800 connector.
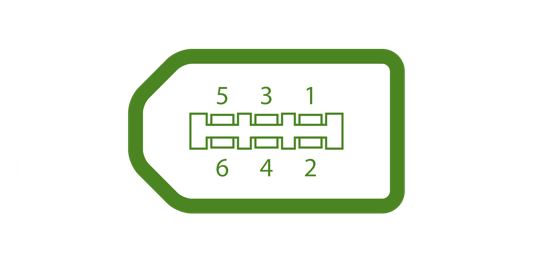
- It can transfer large volumes of data at a very high speed.
- Used to connect video equipment to the computer.
- The data transmission rate is 400 to 800 megabits per second.
- FireWire Port was invented by Apple.
- FireWire has three models: 4-Pin FireWire 400 connector, 6-Pin FireWire 400 connector, and 9-Pin FireWire 800 connector.
The IEEE 1394 interface, which is developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s by Apple as FireWire. It can transfer large amounts of data at very high speed. It is used to connect camcorders and video equipment to the computer. It comes up with three variants which are 4-Pin FireWire 400 connector, 6-Pin FireWire 400 connector, and 9-Pin FireWire 800 connector.

- It can transfer large volumes of data at a very high speed.
- Used to connect video equipment to the computer.
- The data transmission rate is 400 to 800 megabits per second.
- FireWire Port was invented by Apple.
- FireWire has three models: 4-Pin FireWire 400 connector, 6-Pin FireWire 400 connector, and 9-Pin FireWire 800 connector.
8. Infrared Port
An infrared port is a wireless communication interface that is used to send and receive infrared signals from other devices. The range of connectivity of the infrared port is 5-10ft. Infrared port allows devices to communicate without a physical connection.
An infrared port is a wireless communication interface that is used to send and receive infrared signals from other devices. The range of connectivity of the infrared port is 5-10ft. Infrared port allows devices to communicate without a physical connection.
9. Game Port
These ports are used previously to connect a joystick to a PC. But nowadays it is replaced by USB ports.
These ports are used previously to connect a joystick to a PC. But nowadays it is replaced by USB ports.
10. Modem Port
As the name suggests, a Modem port is used to connect a PC’s modem to the telephone network.

As the name suggests, a Modem port is used to connect a PC’s modem to the telephone network.

11. Digital Video Interface(DVI) Port
DVI Port is used to connect an LCD(flat panel) monitor to the computer’s high-end video graphic cards and it is very popular among video card manufacturers.
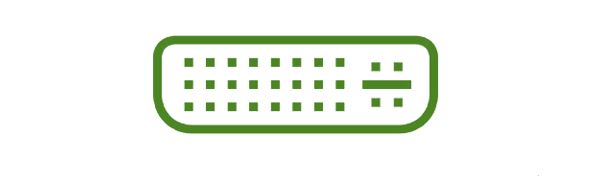
DVI Port is used to connect an LCD(flat panel) monitor to the computer’s high-end video graphic cards and it is very popular among video card manufacturers.

12. Ethernet Port
Ethernet Port helps to connect to a network and high-speed Internet(provided by LAN or other sources). It connects the network cable to a computer and resides in an Ethernet card. It provides a data travel speed of 10 Mb to 1000 Mb(megabits) per second.

- It is used to connect users with LAN (Local Area Network) and provide high-speed internet.
- Connects by using a network cable to a computer.
- The data transmission rate is 10 to 1000 megabits per second depending upon the network bandwidth.
Ethernet Port helps to connect to a network and high-speed Internet(provided by LAN or other sources). It connects the network cable to a computer and resides in an Ethernet card. It provides a data travel speed of 10 Mb to 1000 Mb(megabits) per second.

- It is used to connect users with LAN (Local Area Network) and provide high-speed internet.
- Connects by using a network cable to a computer.
- The data transmission rate is 10 to 1000 megabits per second depending upon the network bandwidth.
Conclusion
As we discussed there are two types of computer ports physical and virtual. These ports are used to connect internal and external devices to the motherboard for communication. Examples of physical ports are USB Ports, Ethernet ports, DVI ports, and many more. Examples of virtual ports include port 20, port 21, port 80, etc.
As we discussed there are two types of computer ports physical and virtual. These ports are used to connect internal and external devices to the motherboard for communication. Examples of physical ports are USB Ports, Ethernet ports, DVI ports, and many more. Examples of virtual ports include port 20, port 21, port 80, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions on Types of Computer Ports – FAQs
What is the full form of USB?
The full form of USB is Universal Serial Bus.
The full form of USB is Universal Serial Bus.
Ethernet Cables are used for ________?
Ethernet cable is used for networking and internet, because ethernet port helps to connect to a network and high speed Internet(provided by LAN or other source).
Ethernet cable is used for networking and internet, because ethernet port helps to connect to a network and high speed Internet(provided by LAN or other source).
Microphone and speakers are connected with the help of________?
Microphone and speakers are connected with the help of Sockets to the sound card of the computer.
Microphone and speakers are connected with the help of Sockets to the sound card of the computer.
FireWire Port is developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s by _______?
The IEEE 1394 interface, which is developed in late 1980s and early 1990s by Apple as FireWire. It can transfer large amount of data at very high speed. It is used to connect camcorders and video equipment to the computer.
The IEEE 1394 interface, which is developed in late 1980s and early 1990s by Apple as FireWire. It can transfer large amount of data at very high speed. It is used to connect camcorders and video equipment to the computer.
In old computers, there is a minimum of how many PS/2 Ports are available?
PS/2 ports are special ports used for connecting old computer keyboard and mouse. In old computers there are minimum two PS/2 Ports, each for the keyboard and the mouse.
PS/2 ports are special ports used for connecting old computer keyboard and mouse. In old computers there are minimum two PS/2 Ports, each for the keyboard and the mouse.
What are the Two versions of Serial ports?
There are two versions of Serial ports, which are 9 pin model and 25 pin model. It transmits data at 115 KB/sec.
There are two versions of Serial ports, which are 9 pin model and 25 pin model. It transmits data at 115 KB/sec.



Comments
Post a Comment